Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM)
Definition: WDM is a short form used for Wavelength Division Multiplexing. It is a technique in which signals of different wavelength are multiplexed together in order to get transmitted over an optical link. The concept of WDM was arrived in 1970.
It is an analog multiplexing technique used in fiber optic communication. Here, optical signals of multiple wavelengths are transmitted using a fiber link.
Basically, the technique acts in a way that signals get combined using a multiplexer (optical combiner) and then allowed to propagate using a single cable. Due to different wavelengths the unwanted mixing of signals is prevented and using a demultiplexer, the signals are then separated and sent to their respective receivers.
WDM System
As we have already discussed that the technique involves combining of optical signals. So, in this section we will discuss how transmission of signal is performed using WDM.
The figure shown below illustrates the WDM system:
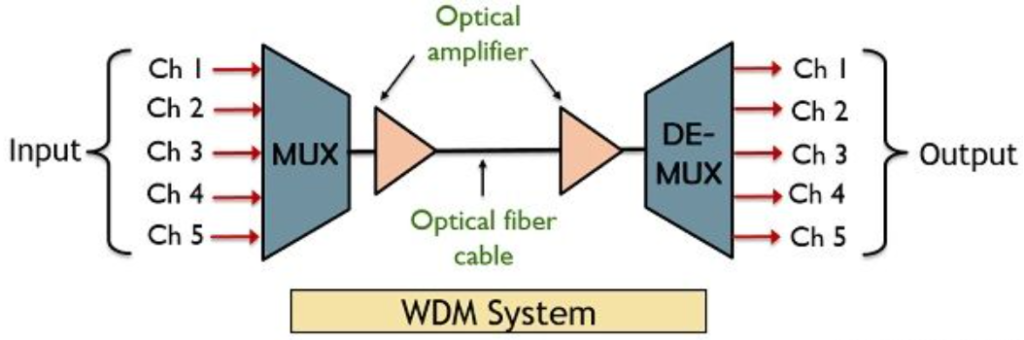
Here as we can see that signals generated from 4 different sources are combined using multiplexer. These multiplexed signals are then allowed to get transmitted over an optical fiber cable.
As the system enables long distance transmission, thus optical amplifiers are installed at some distances between the cables. These amplifiers increase the signal strength in case of long distance transmission.
Once the signal gets propagated then at the other end it must be separated. So, for this a demultiplexer is used to separate the signals at the other end. The demultiplexer separates the combined signal into multiple signals of different wavelengths.
It is to be noted here that a single optical cable offers a bandwidth of about 25,000 GHz. Thus this permits multiplexing of various signals from sources for long distance propagation.
Usually, in wavelength division multiplexing, single mode optical fiber cables are used for signal transmission.
Here’s how WDM works:
1. Multiplexing: In the WDM system, multiple optical signals from different sources are combined for transmission. Each signal is assigned a specific wavelength of light, often in the infrared range, which corresponds to a specific color.
2. Optical Transmitters: The signals from different sources are individually modulated onto laser diodes or other light sources at their respective wavelengths. Each transmitter produces an optical signal with a specific wavelength.
3. Multiplexer: The multiplexer combines the individual optical signals from the transmitters into a single composite signal. It does this by using optical filters or gratings that separate the different wavelengths of light and combine them onto a single fiber.
4. Optical Fiber Transmission: The combined signal, consisting of multiple wavelengths, is then transmitted over a single optical fiber. The fiber carries the signals to the receiving end.
5. Demultiplexer: At the receiving end, a demultiplexer separates the combined signal back into its individual wavelengths. It uses optical filters or gratings to direct each specific wavelength to its respective receiver.
6. Optical Receivers: Each receiver detects and demodulates the individual optical signals at their specific wavelengths. The demodulated signals are then processed further for data extraction or utilization.
WDM technology allows for the simultaneous transmission of multiple signals, such as voice, data, or video, over a single optical fiber, greatly increasing the capacity and bandwidth of the communication system.
Types of Wavelength Division Multiplexing
The WDM technique is mainly classified into two categories:
- CWDM: CWDM stands for Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing. Here the number of channels supported by the system is more as compared to standard wavelength division multiplexing technique.
The different channels are separated at wavelength around 20 nm. It is cost efficient and has the ability to support 18 channels over a single optical link. It is used for distance up to 120 Km which is more than WDM.
The wavelength range in case of CWDM is 1280 nm to 1650 nm. - DWDM: DWDM stands for Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing. This technique supports more number of channel as compared to CWDM. As the number of channels are densely arranged thus it is named so.
The wavelength spacing between the channels is small nearly around 0.4 nm. Also it is comparatively more efficient than both WDM and CWDM.
It supports wavelength range from 1450 nm to 1650 nm.
Advantages of WDM
- WDM is a quite simple technique.
- The optical link provides greater bandwidth.
- It allows secured transmission of optical signal.
- This technique increases the signal carrying capacity of the system.
Disadvantages of WDM
- The presence of optical component increases the overall cost of the system.
- Proper wavelength spacing must be required otherwise it will lead to signal interference.
Application of WDM
The technique of wavelength division multiplexing is used in SONET network, that includes multiplexing and demultiplexing of various optical fiber cables.
Overall, WDM has revolutionized fiber optic communication by enabling high-capacity data transmission, long-haul telecommunications, and efficient utilization of optical infrastructure.
If you have any questions of fiber optic products, please don’t hesitate to contact us.

